elastic recovery hardness test|rockwell hardness scale : agencies Determination of hardness from nanoscratch experiments: Corrections for interfacial shear stress and elastic recovery September 2003 Journal of Materials Research 18(09):2150 - 2162
Sobre a loja. Roupas infantis para colorir a vida, com liberdade para brincar. De 0 a 8 anos ️
{plog:ftitle_list}
31 de jan. de 2012 · Wii Totorial Install NeoGamma R9 Beta 56. Anatoly SAMuel. 473 subscribers. Subscribe. 97. Share. Save. 101K views 11 years ago.
• Elastic behavior: This reversible behavior often shows a linear relation between stress and strain. To minimize deformation, select a material with a large elastic modulus (E or G). • .Elastic behavior: This reversible behavior often shows a linear relation between stress and strain. To minimize deformation, select a material with a large elastic modulus (E or G). Plastic . However, when the test volume displays considerable elastic recovery as the load is removed [e.g., for many stiff hard materials and many inhomogeneous systems (e.g., those employing thin hard . To determine dynamic hardness, the indenter is forced under high loading rate which leads to impact or chock the test material. Thus, the indenter could be shot the tested material like a projectile onto the target surface (Low 2006; El-Ezz 2007).The test material must be permanently deformed, so the kinetic energy should be chosen to assure plastic .
what is rockwell hardness
wermac rockwell hardness
wood macro-indentation hardness testing approaches are Brinell, Vickers, Rockwell, Meyer, Knoop, Shore, Leeb, and Janka. The most widely used test procedures for measuring the hardness of wood materials are the Brinell–Mörath, Janka, and Monnin methods [4], which means that rounded intenders are preferred, those that do not crack the wood. The Determination of hardness from nanoscratch experiments: Corrections for interfacial shear stress and elastic recovery September 2003 Journal of Materials Research 18(09):2150 - 2162
studies of microindentation hardness test results conducted over a wide range of test loads have shown that test results are not constant at very . In the Vickers test, it is assumed that elastic recovery does not occur once the load is removed. however, elastic recovery does occur,
An analytical relationship between the reduced modulus E r and hardness H for solid materials is established based on the conventional depth-sensing indentation method of Oliver and Pharr. It is found that the two properties are related through a material parameter that is defined as the recovery resistance R s.This parameter is shown to represent the energy .
In the original test proposed by Brinell, the load L is expressed in kilogram force. If L is measured in N (SI system), Eq. 1 should be divided by 9.8065. The full test load is applied for a period of 10–15 s. Two diameters of impression at right angles are measured (usually in the range 2–6 mm), and the mean diameter value is used for calculating the Brinell hardness . After being reviewed, the new theory is applied to explain several of the phenomenae associated with practical hardness testing. In the indentation hardness test, a blunt indenter that approximates a flat punch is forced into a plane surface. . When the load is released, the impression remains (except for a small amount of elastic recovery .The low-pressure disordered sp 2-based carbon phases have an interesting combination of high hardness up to 30 GPa and a high elastic recovery and low density (1.6-2.4 g/cm 3). There are two technological advantages in this material.
Simu.latioa of ~licroharduess Testing In order to simulate microhardness testing procedures and explain the influence of elastic recovery on hardness value using the finite element method, we, performed a detailed study of the microhardness testing procedures on 3 typical materials.
The mechanics of hardness indentation are considered. On the basis of a cycle in which the loading is elastic-plastic and the unloading (and subsequent reloading) elastic, an expression is derived for the relative depth recovery of the impression as a function of hardness/modulus,H/E. Experimental observations on indented surfaces of selected materials, mostly ceramics, using .The occurrence of significant elastic recovery (or pile-up) has implications not only for developments in the study of hardness anisotropy of single crystals (e.g. 11,12) but also for the currently developing theories of indentation fracture mechanics where a materials' hardness is assumed to be a Characteristic constant describing the typical . Hard materials are currently characterized by their hardness, H, effective Young's modulus E * =E/(1−ν 2) and elastic recovery W e, where E and ν are the Young's modulus and the Poisson ratio, respectively. For hard coatings, these quantities can easily be determined from loading/unloading curves measured by nanoindentation or instrumented microhardness testing.well as tension, hardness, torsion, and impact tests in particular. Mechanical Testing Mechanical tests (as opposed to physical, electrical, or other types of tests) often involves the deformation or breakage of samples of material (called test specimens or test pieces). Some common forms of test specimens and loading situations are shown in .
Peng et al. [7] established the functional relationship between the elastic recovery and the ratio hardness and Young's elastic modulus through linear regression analyses of the known experimental . Figure 1. Elastic recovery during an indentation process. Symbology - a: indentation radius, h e: elastic recovery; h P: final depth; h: the maximum depth; h C: contact depth and h S: deflected depth.Adapted from .The mechanics of hardness indentation are considered. On the basis of a cycle in which the loading is elastic-plastic and the unloading (and subsequent reloading) elastic, an expression is derived for the relative depth recovery of the impression as a function of hardness/modulus,H/E. Experimental observations on indented surfaces of selected materials, mostly ceramics, using .
rockwell hardness test
The hardness calculated using the extended model was in very close agreement with the accepted value of bulk hardness of fused quartz over the range of scratch depths tested, showing the importance of the effects of elastic recovery and interfacial shear stress. The model was further verified for the case of a pure aluminum sample and the .
hardness test, it is assumed that the indentation does not undergo elastic recovery after force removal. 1 This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E04 on Metallography and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E04.05 on Microindentation Hardness Testing. Current edition approved July 1,Dec. 15, 2007. The 50 kN capacity and the fully variable test speed of 0.2 to 51 mm/min make it possible to perform not only the CBR and Marshall tests, but many other applications as for instance Indirect Tensile test, Quick Triaxial tests, Unconfined and Uniaxial soil testing and, in general, all test to be performed under displacement control.
Nanoindentation and microindentation testing instruments were used. This method was applied to load–unload–reload–unload, multistep, and cycle indentation testing procedures at various hold times and force rates. On unloading the reverse plasticity added to the elastic recovery which increased the apparent elastic modulus.
The hardness calculated using the extended model was in very close agreement with the accepted value of bulk hardness of fused quartz over the range of scratch depths tested, showing the importance of the effects of elastic recovery and interfacial shear stress.Microhardness testing can be defined as indentation hardness testing that involves applied loads of 1 . Additionally, since the area of indentation is measured under load in ultrasonic hardness testing, elastic recovery does not affect the results. A one-point calibration procedure, in conjunction with the ability to measure the contact area .Elastic recovery at hardness indentations B. R. LAWN, V. R. HOWES Department of Applied Physics, School of Physics, University of New South Wales, Kensington, NSW 2033, Australia . When a sharp indenter is loaded onto a flat test specimen it leaves a residual surface impression. A convenient measure of the material hardness may . It has been found that Al3NiTi2 and AlNi2Ti have the highest nano-hardness and elastic recovery rates, while TiAl and GH3039 base metals have the lowest nano-hardness and elastic recovery rates .
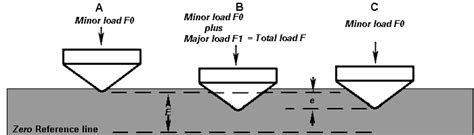
Rockwell Hardness Testing Theory. Rockwell hardness testing has several indenter types which in turn require separate major loads (kg). Figure 1 reflects common Rockwell scales used and their corresponding major loads. Figure 1. When Rockwell hardness testing, a minor load of 10kg is applied to the indenter used on the material being tested.Recovery Test The elastic and viscoelastic recovery of the epoxy composites was evaluated by the percentage of recoverable strain measured after penetration without any external effect during a conventional hardness test. . Elastic recovery at hardness indentations. J. Mater. Sci., 16, 2745–2752. 8. Lorenzo, V., Perena, J. M., Fatou, J. G .
14 de jun. de 2023 · Spela casino gratis spiele, spela casino bonus ohne einzahlung Spela casino gratis spiele Spela casino gratis spiele How to choose a casino Games of chance: RTP and variance Bonuses and promotions Fair gambling codex Responsible gambling and help for problem gamblers, spela casino gratis spiele. Die
elastic recovery hardness test|rockwell hardness scale